React Study - ES6
— React, ReactNative, TIL — 1 min read
ES6
강의에서 친절하게 설명안해줘서 ..설명은 이 글 을 참조하였다.
MDN web doc 에서도 자세한 설명들이 많음.
Bable 이란?
바벨은 다음버전의 자바스크립트 문법을 현재 사용가능한 문법으로 변환시켜주는 역할을 한다. ES6는 또뭐냐 ..?? ECMAScript 란 자바스크립트를 이루는 코어 스크립트 언어이다. 이것을 ES라고 줄여 부르고 6는 버전명이다.Babel 로컬 환경설정
1. Babel-cli 와 babel-node 설치(web storm)
1npm install --save-dev babel-cli- 설치후 webstrom 실행
Preference > Tool > File Watcher 에 이동
"+" 버튼을 누르고 Babel 추가
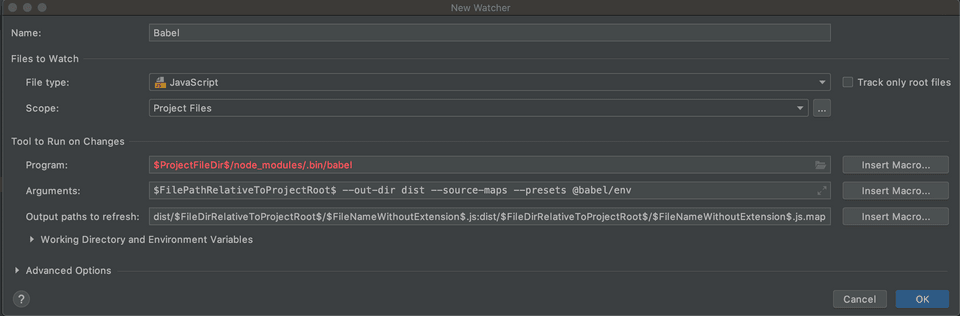
- .babelrc config 파일 생성
1npm install @babel/preset-env --save-devwebstorm 이외의 방법은 Babel install 홈페이지에 자세히 나와있다.
2. npx 설치
script 를 안만들어도 실행시켜주는 역할을 함.
1npm install -g npxString literal
const 와 let가 있다.
Swift 에서는 let 가 상수인데 ES6에서는 let가 변수이다.
const 를 기본으로 사용하고, const는 값의 재할당이 불가능하다.
문자열 더하기는 + 또는 ${}로 표현가능. conVal 과 litVal은 출력값이 같다.
1const val1 = 'string1';2const val2 = 'string2';3
4const conVal = val1 + ',' + val2;5const litVal = `${val1}, ${val2}`let, const
기존의 javascript 에는 var만 존재했음.
Const : 값의 재할당이 불가능함. 객체 안의 변수는 재할당이 가능한데 그 자체를 바꾸는 것은 불가능.
hoisting : scope 가 다른데 접근이 되는것.
1// let & const2const myId = "coooldoggy";3
4// var is hoisting5// ECMA Script 2015 = es66console.log(myId);7if (true) {8 let myId = 'dooboolab';9}10
11// const12// object13const fruit = {};14fruit.first = 'apple';15console.log(fruit);16// array17const apples = [0, 1, 2];18apples[0] = 5;19console.log(apples);객체 비구조화 Object Destructuring
객체에서 필요한 것 만 가져오는것 address 객체에서 country 값만 가져옴
1const address = {2 country: 'South Korea',3 city: 'Seoul',4 street: 'GangNam',5 str_num: 1416}7
8const{ country } = address;배열 비구조화 Array Destructuring
Object 만큼 유연하지 않음. 순서대로 출력
1const name [first, second, thrid] = ['Japan', 'South Korea', 'America'];2
3let [name1] = name;4console.log(name1); //Japan객체 리터럴 Object Literal
1function getAddress(country, city, street){2 const myAddress = {country, city, street};3 console.log(myAddress);4}5
6getAddress('South Korea', 'Seoul', 'street');For.. Of문
Java 의 For in 문과 비슷함.
JavaScript 의 For.. in 문에서는 index 순회를 함으로 배열에 없는 상위 프로토타입의 값도 포함될 수 있지만 For..of 문에서는 value순회를 하여 이와같은 문제를 방지할 수 있다.
1let years = [2001, 2010, 2015, 2018];2
3for (let year of years){4 console.log(year)5}Spread Operator
... <- 이거
1let years = [2001, 2010, 2015, 2018];2let yearsCp = [...years];3//앞뒤에도 추가해서 복사가능4let addyearsCp = [2000, ...years, 2020];5
6console.log(yearsCp)7
8let koreanHistory = {9 liberate: 1945,10 625: 1950,11};12
13let history = {14 worldWar1: 1914,15 worldWar2: 1945,16 ...koreanHistory,17}18
19let address1 = {20 country: 'South Korea',21 citiy: 'Seoul',22};23
24let address2 = {25 ...address1,26 country: 'United State',27};28console.log(address2);Rest Operator
자주 쓰이지는 않음
1// past2 function printYears(years) {3 console.log(years); //20004 console.log(arguments); // {0: 2000, 1:2001, 2: 2010, 3:2015, 4: 2018}5 }6
7// now8function printYears(...years) {9 console.log(years); //2000, 2001, 2010, 2015, 201810}11
12printYears(2000, 2001, 2010, 2015, 2018);Arrow Function
function 표현에 비해 구문이 짧다. 항상 익명 함수로 사용됨.
메소드 함수가 아닌곳에 적합하기 때문에 생성자로 사용할 수 없음.
1// Arrow Functions2const years = [3 {4 year: 2000,5 data: '크리스마스',6 },7 {8 year: 2001,9 data: '롤리팝',10 },11 {12 year: 2010,13 data: '안드로이드',14 },15 {16 year: 2015,17 data: '리엑트네이티브',18 },19 {20 year: 2018,21 data: '곧 2019',22 },23];24
25// past26// const result = years.filter(function (data) {27// return data.year > 2000;28// });29
30// arrow function31const result = years.filter((data) => data.year > 2000);32
33console.log(result);Default Params
Default 파라미터를 함수에 정해주는 것.
1// Default Params2const defaultValue = [3 {4 year: 2000,5 data: '크리스마스',6 },7 {8 year: 2001,9 data: '롤리팝',10 },11 {12 year: 2010,13 data: '안드로이드',14 },15 {16 year: 2015,17 data: '리엑트네이티브',18 },19 {20 year: 2018,21 data: '곧 2019',22 },23];24
25function printYears(years = defaultValue) {26 console.log(years);27}28
29printYears();Includes
배열에 사용. 배열이 특정 요소를 포함하고 있는지를 판별한다.
1// includes2// let years = [2001, 2010, 2015, 2018];3const fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'potato'];4
5// past6// console.log(years.indexOf(2001) !== -1);7// console.log(fruits.indexOf('apple') !== -1);8
9console.log(fruits.includes('apple'));Import, Export
1import root from './includes';2import { fruits } from './includes';3console.log(root);4console.log(fruits);5
6export default friuts;Classes
1// Classes2// es53// function Animal () {4// this.type = 'chosic';5// this.tail = false;6// }7
8// Animal.prototype.setType = function(type) {9// this.type = type;10// }11
12// Animal.prototype.getType = function() {13// return this.type;14// }15
16// es617class Animal {18 // constructor19 constructor(type, tail) {20 this.type = type;21 this.tail = tail;22 }23
24 // function25 cry(value = 'Woof Woof') {26 console.log(value);27 }28
29 // static function30 static instance() {31 console.log('instance!!');32 }33}34
35let dog = new Animal('Dog', true);36dog.tail = false;37console.log(dog);38
39dog.cry('woof');40
41// inheritance42class Cat extends Animal {43 constructor(type, tail, color) {44 super(type, tail);45 this.color = color;46 }47 cry(value = 'Meow Meow') {48 console.log(value);49 }50}51
52let cat = new Cat('Cat', true, 'yellow');53cat.cry();54console.log(cat);Trailing Commas
새로운 엘리먼트나 매개변수, 속성을 추가할 때 유용함.
마지막에 , 를 붙여주는 것을 허용하는 것.
1// Trailing Commas2const myObj = {3 first: 'test1',4 second: 'test2',5};6
7console.log(myObj);8
9const myArr = [10 1,11 2,12 3,13 3,14 3,15 3,16 3,17];18console.log(myArr);Map, Set
key, value 의 쌍으로 이뤄져있음
1// Map2let map = new Map([['id', 'dooboolab']]);3map.set('testId', 'test');4map.get('testId'); // test5console.log(map);6console.log(map.size);7
8console.log(map.has('testId'));9console.log(map.entries()); //전체 값을 보는것10console.log(map.keys());11console.log(map.values());12console.log(map.delete('testId'));13console.log(map.size);14map.clear();15console.log(map.size);16
17// Set18const set = new Set([1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2,2,2,3,3]);19set.add(4);20set.add(4).add(5);21console.log(set);22console.log(set.size);23
24set.delete(5);25console.log(set.size);26set.clear();27console.log(set.size);Async, Wait
javascript 의 callback 지옥을 해결해줌.
1function resolvePromise() {2 return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {3 setTimeout(() => {4 resolve('done!!');5 }, 2000);6 });7}8
9async function getPromise1() {10 const result = await resolvePromise();11 console.log(result);12 await resolvePromise();13 console.log(result);14 await resolvePromise();15 console.log(result);16 await resolvePromise();17 console.log(result);18 await resolvePromise();19 console.log(result);20 await resolvePromise();21 console.log(result);22 await resolvePromise();23 console.log(result);24}25
26getPromise1();